June 26, 2024
The Life Cycle of Naphtha: From Refining to End Products
Naphtha, a versatile hydrocarbon mixture derived from crude oil refining, plays a crucial role in various industries worldwide. From its initial extraction during the refining process to its transformation into essential end products, naphtha undergoes a complex life cycle that supports diverse applications across energy, petrochemicals, and manufacturing sectors.
In this blog, we will explore the journey of naphtha from refining through to its final uses, highlighting its significance in modern industrial processes.
Introduction to Naphtha
Naphtha is a light to medium-weight hydrocarbon fraction typically obtained from the atmospheric distillation of crude oil. It consists of a complex mixture of aliphatic and aromatic compounds, with boiling points ranging between 30°C to 200°C. Due to its composition, naphtha serves as a feedstock for various downstream processes, making it a valuable commodity in the global energy and petrochemical markets.
Naphtha is a complex mixture of liquid hydrocarbons, typically containing carbon compounds ranging from C5 to C9. It is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture that can be derived from crude oil, natural gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the fractional distillation of coal tar and peat. Naphtha can be categorized into different types based on factors like molecular makeup and boiling point, such as light naphtha (C5-C6) and heavy naphtha (C6-C12).
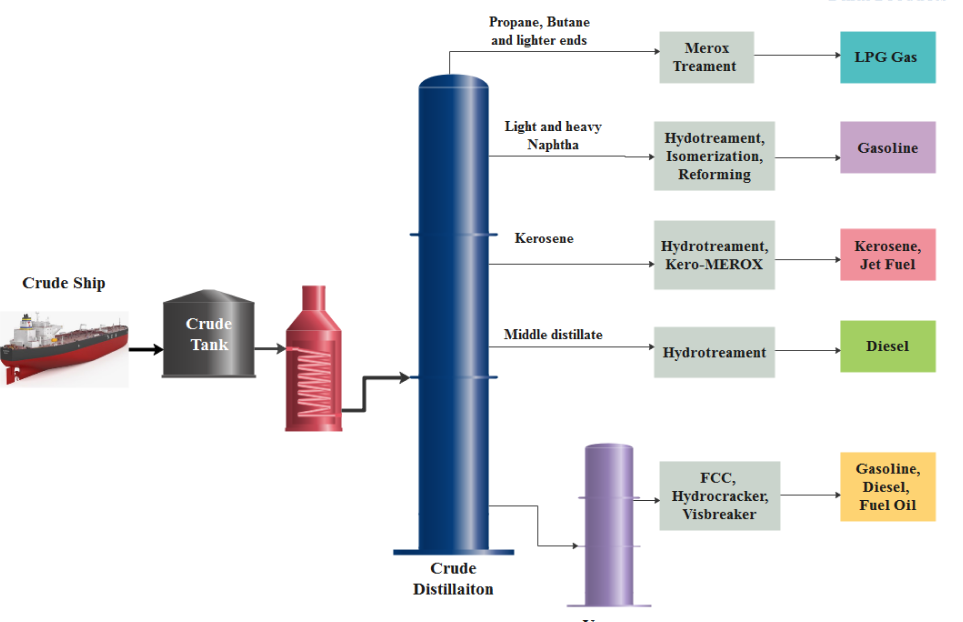
Refining Process
The life cycle of naphtha begins with its extraction during the refining of crude oil:
Distillation: Crude oil is heated in a distillation tower, where it separates into fractions based on boiling points. Naphtha is collected as one of the lighter fractions above kerosene and diesel.
Fractionation: Further refining processes, such as catalytic reforming or hydrotreating, may be employed to enhance naphtha’s quality and adjust its chemical composition for specific applications.
Catalytic Reforming: Naphtha may undergo catalytic reforming, a process that utilizes catalysts (special substances that accelerate reactions) to increase the octane rating of the product. This “reformed” Naphtha becomes a valuable blending stock for high-quality gasoline. (Consider including a simplified diagram of a catalytic reformer).
The most significant transformation of Naphtha lies in a process called cracking. Here, Naphtha is subjected to high temperatures and often catalysts, causing its long hydrocarbon chains to break down into smaller, lighter molecules. This process, known as naphtha cracking. This process can be helpful for the production of various materials like Ethylene, Propylene, etc.
Application
Petrochemical Applications: Naphtha is a vital feedstock for the petrochemical industry, where it is primarily used to produce Various materials:
- Ethylene and Propylene: Through steam cracking, naphtha undergoes thermal decomposition to yield ethylene and propylene, which serve as building blocks for plastics, synthetic fibers, and other polymers.
- Aromatics: Naphtha reforming processes produce aromatic compounds like benzene, toluene, and xylene, which are essential for manufacturing plastics, solvents, and synthetic rubbers.
Manufacturing of Fuels: In addition to its role in petrochemicals, naphtha is also utilized in the production of fuels:
- Gasoline: Light naphtha fractions are blended into gasoline to enhance octane ratings and improve combustion properties.
- Aviation Fuels: Certain naphtha fractions contribute to the formulation of jet fuels, ensuring optimal performance in aircraft engines. End Products and Consumer Goods
Beyond industrial applications, naphtha derivatives contribute to everyday consumer goods:
- Solvents: Naphtha-based solvents are used in paints, coatings, and cleaning products for their ability to dissolve oils, resins, and other substances.
- Adhesives and Sealants: Naphtha derivatives serve as key ingredients in adhesives and sealants, providing bonding strength and flexibility.
- Asphalt Industry: Naphtha is used in the production of asphalt by refining crude oil and by processing petroleum products. Naphtha can help thin or liquefy very thick or cold asphalt, making it easier to transport, pump, and
apply during paving operations. - New Industries: The aerospace industry is adopting naphtha for manufacturing aircraft components, such as commercial and defense aircraft. The renewable energy industry is adopting naphtha as a feedstock for bio-based products, such as bio-naphtha and bio-ethanol, to reduce carbon footprint.
Environmental Considerations
While naphtha supports numerous industrial processes and product applications, its refining and utilization raise environmental considerations:
Emissions: Processing and combustion of naphtha-based fuels contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants.
Spills and Contamination: Accidental spills of naphtha can lead to soil and water contamination, necessitating stringent safety measures and environmental management practices.
Future Outlook and Sustainability
Efficiency: Continuous improvements in refining technologies aim to maximize naphtha yield and quality while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Sustainability: To address these sustainability challenges, the industry is exploring alternative sources and production methods for naphtha. One promising avenue is the development of bio-based naphtha, derived from renewable feedstocks such as agricultural waste or biomass. These bio-naphtha products can offer a more environmentally friendly alternative, with the potential to reduce the carbon intensity of naphtha-dependent industries.
Another area of focus is the optimization of naphtha production processes to improve energy efficiency and minimize waste. Advancements in catalytic technologies, distillation techniques, and process integration can help enhance the overall sustainability of naphtha manufacturing.
Conclusion
Naphtha’s journey from crude oil refining to its diverse applications underscores its critical role in modern industry and everyday life. As a versatile feedstock for petrochemicals, fuels, and consumer goods, naphtha continues to drive innovation and economic growth globally. By embracing technological advancements and sustainability initiatives, industries can harness the potential of naphtha while addressing environmental challenges and meeting evolving consumer demands.
Explore the dynamic life cycle of naphtha and its impact on industry and society. From refining to end products, naphtha exemplifies the intricate interplay between science, technology, and sustainability in today’s global economy.


